WHAT IS A PNEUMATIC SYSTEM?]
🎙️ Voiceover:
“A pneumatic system is a type of power transmission system that uses compressed air or gas to perform mechanical work. These systems are widely used due to their simplicity, reliability, and cost-effectiveness compared to hydraulic and electrical systems.”
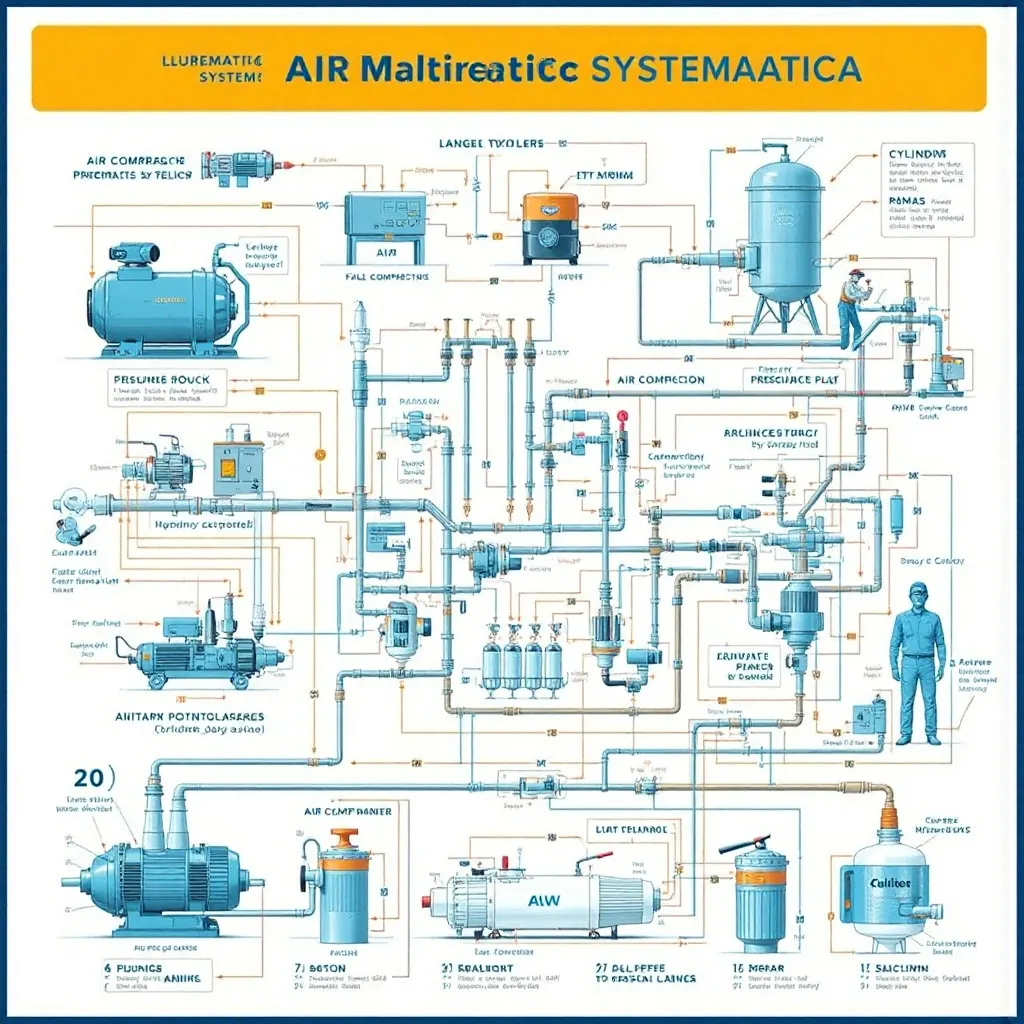
Key Components of a Pneumatic System
(Infographic: Breakdown of components with labeled animation)
Air Compressor – Generates compressed air.
Reservoir/Tank – Stores compressed air for stable operation.
Pressure Regulator – Controls air pressure to prevent damage.
Valves (Directional, Flow, Pressure Control) – Direct and regulate air movement.
Actuators (Cylinders, Motors) – Convert air pressure into mechanical motion.
Piping and Fittings – Transport air within the system.
Filters and Lubricators – Ensure clean, moisture-free air for smooth operation.
[HOW DOES A PNEUMATIC SYSTEM WORK?]
🎙️ Voiceover:
“The working principle of a pneumatic system follows a simple energy conversion process. Compressed air is stored in a reservoir, regulated, and directed through valves to actuators, which generate motion.”
Working Steps:
Compression: Air is compressed by an air compressor.
Storage: Compressed air is stored in a tank or receiver.
Control: Regulators and valves adjust pressure and flow.
Actuation: Cylinders or motors move based on controlled airflow.
Exhaust: Used air is expelled after performing work.
(Infographic Animation: Airflow moving through a pneumatic system to actuate a piston)
[TYPES OF PNEUMATIC SYSTEMS]
🎙️ Voiceover:
“There are several types of pneumatic systems, classified based on their application and functionality.”
- Based on Actuation Type
✅ Single-Acting Pneumatic System – Uses air pressure in one direction; return motion is spring-driven.
✅ Double-Acting Pneumatic System – Uses air pressure in both directions for better control. - Based on Pressure Levels
✅ Low-Pressure Pneumatic Systems – Up to 1.5 bar for light-duty applications.
✅ Medium-Pressure Pneumatic Systems – 1.5 to 10 bar, commonly used in industrial automation.
✅ High-Pressure Pneumatic Systems – Above 10 bar, used in heavy machinery and special industries. - Based on Application
✅ Industrial Automation Pneumatics – Used in assembly lines, robotics, and conveyor systems.
✅ Medical and Healthcare Pneumatics – Found in ventilators, dental tools, and lab automation.
✅ Aerospace and Defense Pneumatics – Used in aircraft landing gears, missile launchers, and braking systems.
(Infographic showing examples of each type with real-world visuals)
[APPLICATIONS OF PNEUMATIC SYSTEMS]
🎙️ Voiceover:
“Now, let’s explore the real-world applications of pneumatic systems across various industries.”
🚗 Automotive Industry – Used in brakes, suspension systems, robotic assembly arms.
🏭 Manufacturing & Automation – Found in press machines, conveyor belts, pick-and-place systems.
🛫 Aerospace & Defense – Used for aircraft landing gear operation, missile launch mechanisms.
🦷 Medical & Healthcare – Pneumatic tools for dental drills, oxygen regulators, ventilators.
🍔 Food & Beverage Industry – Packaging machines, food processing lines, bottling plants.
(Infographic with a montage of different industries using pneumatics)
[STANDARDS & SAFETY REGULATIONS]
🎙️ Voiceover:
“Pneumatic systems must follow strict safety and performance standards to ensure efficiency and workplace safety. Some key industry standards include:”
🛠️ ISO 8573 – Governs compressed air purity.
🛠️ ANSI B93.9 – American standards for pneumatic components.
🛠️ DIN ISO 1219 – German standard for fluid power symbols.
🛠️ NFPA 79 – Electrical safety standard for industrial machinery.
🛠️ OSHA Regulations – Ensures workplace safety for pneumatic system usage.
(Infographic listing standards with country flags)
[TOP PNEUMATIC SYSTEM MANUFACTURERS]
🎙️ Voiceover:
“Here are some of the leading pneumatic system manufacturers worldwide:”
🏢 Festo – Leading German company specializing in industrial automation.
🏢 SMC Corporation – Japanese manufacturer known for high-precision pneumatic components.
🏢 Parker Hannifin – American company specializing in motion control technologies.
🏢 Bosch Rexroth – German automation leader in pneumatics and hydraulics.
🏢 Aventics (Emerson) – U.S.-based manufacturer of industrial pneumatic solutions.
(Infographic with logos and headquarters locations)
[ADVANTAGES & DISADVANTAGES OF PNEUMATIC SYSTEMS]
🎙️ Voiceover:
“Before we conclude, let’s quickly look at the advantages and disadvantages of pneumatic systems.”
✅ Advantages:
✔️ Cost-effective & energy-efficient.
✔️ Safe to use in hazardous environments.
✔️ Requires less maintenance than hydraulic systems.
✔️ Simple & easy to install.
❌ Disadvantages:
❌ Not suitable for high-force applications.
❌ Compressors require energy and produce noise.
❌ Air leakage can reduce efficiency.
(Animated comparison of pneumatic, hydraulic, and electric systems)
[CONCLUSION]
🎙️ Voiceover:
“Pneumatic systems are a vital part of modern industries, offering a reliable, efficient, and safe method for automation and motion control. Whether in automotive, aerospace, medical, or manufacturing sectors, these systems help streamline production and improve efficiency. Understanding their types, applications, and safety standards is crucial for engineers and industries.”
📢 If you found this video helpful, hit the like button and subscribe to Factory Flow for more industrial insights!
[END SCREEN]
✅ Subscribe to Factory Flow 🔔
✅ Watch More Industrial Automation Videos 📺
✅ Follow Us for More Updates
A pneumatic system is a type of power transmission system that uses compressed air or gas to generate mechanical force and motion. It’s a versatile technology used across many industries due to its simplicity, reliability, and cost-effectiveness compared to hydraulic and electrical systems.
Here’s a breakdown of the key aspects:
How it Works:
A pneumatic system works by compressing air, storing it under pressure, and then using that pressurized air to power actuators (like cylinders or motors). Valves control the flow and direction of the compressed air, allowing for precise and controlled movement. After the work is done, the used air is exhausted.
Key Components:
- Air Compressor: Compresses atmospheric air to create high-pressure air.
- Reservoir/Tank: Stores the compressed air, providing a stable supply.
- Pressure Regulator: Controls and maintains the desired air pressure.
- Valves: Direct and control the flow of compressed air. There are various types, including directional control valves, flow control valves, and pressure control valves.
- Actuators: Convert the compressed air energy into mechanical movement. These can be pneumatic cylinders (linear motion) or pneumatic motors (rotary motion).
- Piping and Fittings: Connect the components and transport the compressed air.
- Filters and Lubricators: Clean and lubricate the compressed air to prevent damage and ensure smooth operation.
Types of Pneumatic Systems:
Pneumatic systems are categorized based on actuation type, pressure levels, and application:
- Actuation Type: Single-acting (uses air pressure in one direction, return is spring-powered) and double-acting (uses air pressure in both directions for more precise control).
- Pressure Levels: Low-pressure (up to 1.5 bar), medium-pressure (1.5 to 10 bar), and high-pressure (above 10 bar).
- Application: Industrial automation, medical, aerospace, and more.
Advantages and Disadvantages:
Advantages:
- Cost-effective
- Relatively energy-efficient
- Safe in hazardous environments
- Easy to install and maintain
Disadvantages:
- Limited force capabilities compared to hydraulics
- Compressors are noisy and require energy
- Susceptible to air leaks, reducing efficiency
Applications:
Pneumatic systems are used extensively in:
- Automotive industry (brakes, suspension)
- Manufacturing and automation (robotics, assembly lines)
- Aerospace and defense (landing gear, missile launchers)
- Medical and healthcare (dental tools, ventilators)
- Food and beverage industry (packaging machines)
#chats