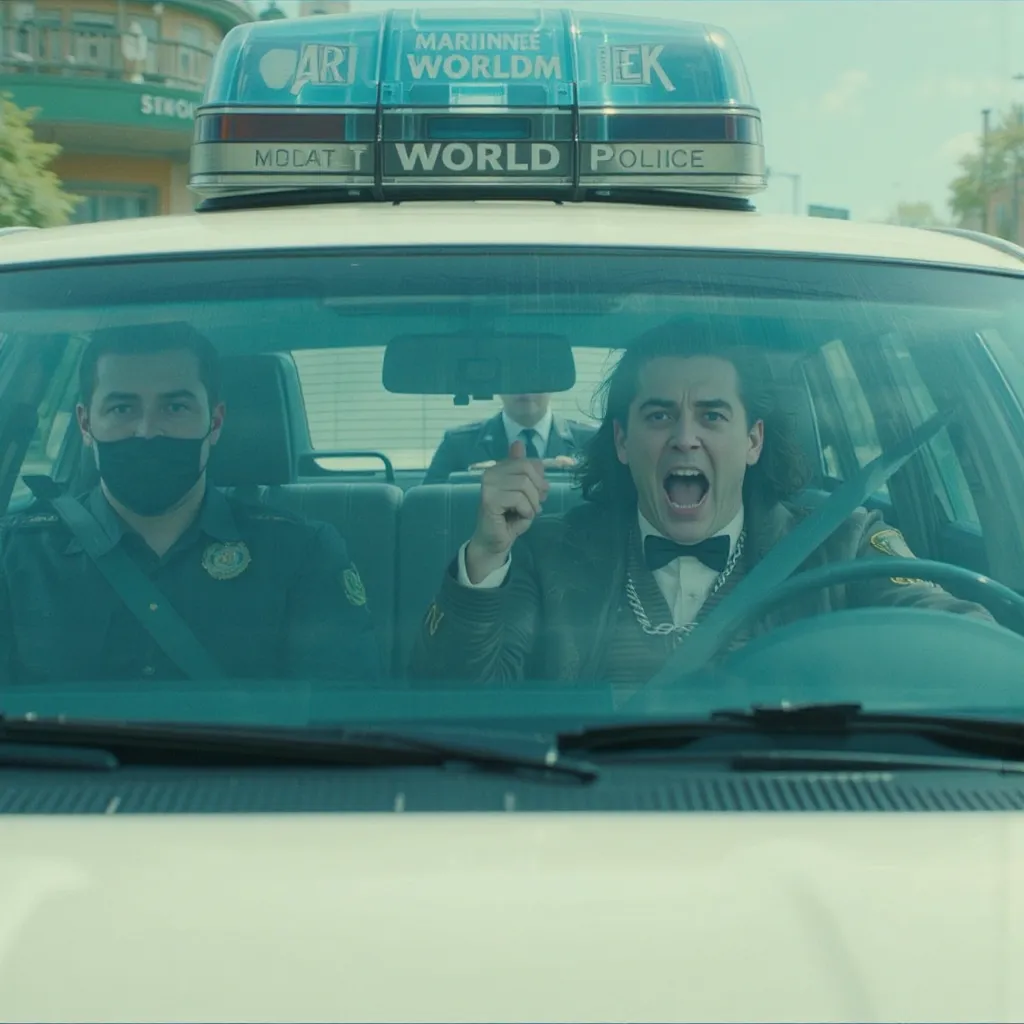
At the Maryland District Court in Rockville MD, a cival trial has come to order, Miss Frizzle was suing Sid the Science Kid for stealing her bus, taking her and the kids on a wreckless driving spree and using them to steal from a jewerly store in Baltimore MD
Okay, the gavel slams down in the Maryland District Court in Rockville. All rise! Judge Thompson, a woman with a no-nonsense expression and a sensible pantsuit, enters the courtroom.
“All right, settle down,” she says, adjusting her glasses. “We’re here today for the case of Ms. Valerie Frizzle versus Mr. Sidney… uh… ‘the Science Kid’? Is that correct?”
A woman with bright red, frizzy hair that seems to defy gravity – Ms. Frizzle – nods emphatically. She’s wearing a dress covered in planets and constellations. Beside her, a somewhat bewildered-looking lizard in a tiny suit (presumably her lawyer) adjusts his tie.
On the other side of the courtroom, a young boy with a perpetually curious expression and oversized sneakers – Sid the Science Kid – fidgets nervously. His lawyer, a weary-looking public defender, pats him on the back reassuringly.
“Ms. Frizzle,” Judge Thompson says, “you’re claiming that Mr. ‘Science Kid’ stole your bus, took you and your students on a ‘reckless driving spree,’ and used you all to… rob a jewelry store in Baltimore? Is that a fair summary?”
“Absolutely, Your Honor!” Ms. Frizzle exclaims. “It was a chaotic, dangerous, and frankly, criminal misuse of science! He hijacked the Magic School Bus! He endangered my students! And he used advanced scientific principles to… well, let’s just say the Baltimore jewelry store is missing a rather large diamond necklace.”
Sid shrinks in his seat. “But… but it was for science!” he protests. “I was just trying to understand the refractive properties of diamonds under extreme gravitational stress! And the bus… well, it’s the perfect vehicle for scientific exploration!”
Judge Thompson sighs. “Mr. ‘Science Kid,’ I suspect this is going to be a very long day.”

Miss Frizzle’s class is in the courtroom in the adiaunce as well as Fred Jones who witness the robbery, the 1st witness called was the CEO of Samuelson’s Diamonds & Estate Buyers in Baltimore MD-Ron Samuelson
Okay, back in the Rockville courtroom, tension is thick enough to cut with a beaker. Judge Thompson calls for order. “Alright, alright. Let’s get down to business. Ms. Frizzle, you may call your first witness.”
Ms. Frizzle, with a dramatic flourish, points towards a distinguished-looking gentleman with a neatly trimmed beard. “Your Honor, I call Mr. Ron Samuelson, CEO of Samuelson’s Diamonds & Estate Buyers in Baltimore!”
Ron Samuelson, looking understandably perturbed, takes the stand. He’s sworn in, and Ms. Frizzle approaches him with a mischievous glint in her eye.
“Mr. Samuelson,” she begins, “could you please describe the events of the afternoon of July 12th, specifically concerning the disappearance of a certain… sparkly item?”
Samuelson clears his throat. “Well, it was a normal Tuesday afternoon. Customers browsing, the usual security measures in place. Then… they arrived.” He gestures vaguely in Sid’s direction. “There was a school bus parked rather oddly outside, and then suddenly… chaos. Flashing lights, strange contraptions, and a group of children running around asking about the refractive index of various gemstones.”
“And the necklace, Mr. Samuelson? The ‘Empress Diamond’ necklace, valued at approximately $2.5 million?” Ms. Frizzle presses.
“Gone,” Samuelson says grimly. “Vanished. Along with a faint scent of… ozone and bubblegum.”
Just then, a familiar voice pipes up from the audience. “Like, zoinks! I saw the whole thing!” It’s Fred Jones, the iconic member of Mystery Inc., looking surprisingly out of place in a courtroom. “That kid, Sid, he had some kind of science gizmo that made the necklace disappear! It was totally bizarre!”
Sid’s lawyer throws his hands up in exasperation. “Your Honor, I object! This is circumstantial at best! My client is a budding scientist! He was merely conducting research!”
Judge Thompson bangs her gavel. “Order! Order in the court! Mr. Jones, please refrain from interjecting unless called upon. Ms. Frizzle, proceed.”
Ms. Frizzle smiles, a mischievous glint in her eye. “Oh, I intend to, Your Honor. I intend to.”

Soon Sid the Science Kid was put on the stand, he soon say he hopes to get payback some day
Back in the Rockville courtroom, the spotlight shifts to Sid the Science Kid as he’s called to the stand. He shuffles forward, looking significantly less confident than usual. His oversized sneakers squeak on the polished floor.
“Mr. ‘Science Kid’,” Judge Thompson says, her voice laced with a hint of weariness, “you’ve heard the testimony. Mr. Samuelson claims you stole a valuable necklace. Ms. Frizzle claims you endangered her students. What do you have to say for yourself?”
Sid fidgets, pushing his large glasses up his nose. “Well, Your Honor, it’s not exactly stealing. It was more of a… temporary acquisition for scientific purposes.”
“Temporary acquisition? Mr. Samuelson’s necklace is still missing!” Judge Thompson raises an eyebrow.
“But the science!” Sid exclaims. “The refractive properties of diamonds under extreme gravitational stress are fascinating! I needed the Empress Diamond to complete my experiment! The Magic School Bus is perfect for creating a controlled environment for these experiments. Ms. Frizzle just didn’t understand the importance of scientific discovery!”
Ms. Frizzle scoffs from her table. “Endangering children and robbing jewelry stores is not scientific discovery, Sidney!”
Sid hangs his head. “Okay, maybe the bus driving was a little reckless. And maybe the gravitational stress caused a minor temporal displacement of the necklace…”
“Temporal displacement?” Judge Thompson repeats slowly. “Are you saying you sent the necklace… through time?”
“Uh… maybe?” Sid mumbles, avoiding eye contact.
Suddenly, Sid’s demeanor changes. A flicker of anger crosses his face. He leans into the microphone. “And when I get out of here,” he says, his voice surprisingly steely, “I’m going to get payback on everyone who doubted my science!”
His lawyer gasps, burying his face in his hands. Ms. Frizzle stares at Sid, a mixture of shock and concern on her face. Fred Jones whispers something to Scooby-Doo, who whimpers.
Judge Thompson bangs her gavel with renewed force. “Order! Order! I think we’re done here for the day. Court is adjourned!”

The next day, the jury returned the verdict, they ruled in favor of Miss Frizzle, Sid will have to $1,000,000 to Samuelson, and a $5,000,000 bill to the Walkerville Elementry School for damages and emiotial distress
The Rockville courtroom is packed again, buzzing with anticipation. Judge Thompson enters, her expression unreadable.
“Ladies and gentlemen of the jury,” she says, her voice cutting through the murmurs, “have you reached a verdict?”
The foreman, a middle-aged woman with a serious demeanor, stands. “Yes, Your Honor. We have.”
A hush falls over the room.
“In the matter of Valerie Frizzle versus Sidney ‘the Science Kid’,” the foreman continues, “we find in favor of the plaintiff, Ms. Frizzle.”
A collective gasp ripples through the audience. Ms. Frizzle pumps her fist in the air, while Sid slumps in his chair, his lawyer looking utterly defeated.
“Furthermore,” the foreman says, “we award damages as follows: $1,000,000 to Samuelson’s Diamonds & Estate Buyers to compensate for the loss of the Empress Diamond necklace.” Ron Samuelson nods grimly.
“And,” the foreman continues, “we award $5,000,000 to Walkerville Elementary School to cover damages to the Magic School Bus, emotional distress suffered by the students, and for the general disruption to the learning environment.” Ms. Frizzle embraces her lizard lawyer, who looks surprisingly pleased.
Judge Thompson bangs her gavel. “So ordered. Mr. ‘Science Kid’, you are responsible for paying these damages. Court is adjourned.”
As the courtroom empties, Sid sits alone, staring blankly ahead. The weight of the verdict seems to crush him. He mutters to himself, “But… the science… it was all for science…”

Soon the judge orders the bailiffs to arrest Sid for kidnapping and robbery
The Rockville courtroom erupts in chaos. Sid, still reeling from the verdict, looks up in confusion as Judge Thompson slams her gavel again.
“Order! Order in the court!” she booms. “Based on the evidence presented, and Mr. ‘Science Kid’s’ own admission of reckless endangerment and… temporal displacement… I am ordering the bailiffs to take Mr. Sidney ‘the Science Kid’ into custody on charges of kidnapping and robbery.”
Two burly bailiffs immediately move forward, flanking Sid. He struggles weakly, protesting, “But it was for science! You can’t arrest me for science!”
His lawyer, looking utterly defeated, simply shakes his head. Ms. Frizzle watches with a complicated expression, a mixture of relief and pity on her face. She whispers something to her lizard lawyer, who nods in agreement.
As the bailiffs lead Sid away, Judge Thompson addresses the court. “This case should serve as a reminder that even the pursuit of knowledge must be tempered with responsibility and respect for the law. Court is adjourned!”
The courtroom slowly empties, leaving behind the echoes of a bizarre and unforgettable trial. The fate of Sid the Science Kid now rests in the hands of the justice system.

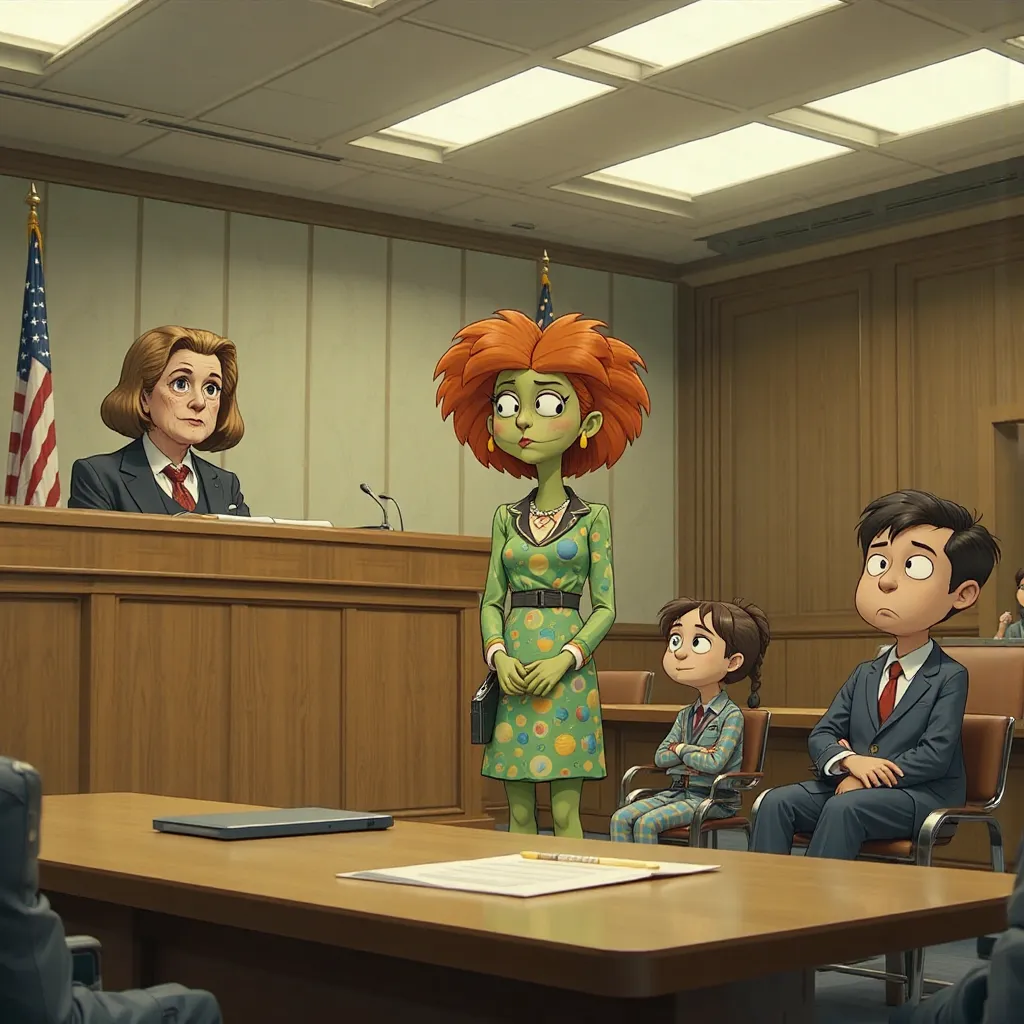
2 months later, the trial for Sid the Science Kid was held at the Edward A. Garmatz United States District Courthouse in Baltimore MD, a 12 person jury was seated, Ivan J. Bates-State’s Attorney for Baltimore City was the DA and Honorable Melissa Copeland was the judge, the 1st witness called was Miss Frizzle
Two months have passed. The scene shifts from Rockville to the imposing Edward A. Garmatz United States District Courthouse in Baltimore, Maryland. The air is thick with anticipation as the trial of Sidney “the Science Kid” commences. Inside the courtroom, Honorable Melissa Copeland presides, her gaze sharp and unwavering. Representing the state is Ivan J. Bates, the State’s Attorney for Baltimore City, a man known for his meticulous preparation and relentless pursuit of justice. A 12-person jury sits attentively, their faces a mix of curiosity and apprehension.
Bates rises, his voice resonating through the courtroom. “Your Honor, the state calls its first witness, Ms. Valerie Frizzle.”
Ms. Frizzle, looking more subdued than before, takes the stand. Her vibrant dress is replaced with a more somber, professional attire, though her signature fiery red hair remains untamed. She’s sworn in, and Bates approaches her with a practiced smile.
“Ms. Frizzle,” he begins, “can you please describe your relationship with the defendant, Sidney ‘the Science Kid’?”
Ms. Frizzle hesitates, a flicker of sadness in her eyes. “Sidney was one of my students. A bright, inquisitive student. He had a passion for science, but… his methods were, shall we say, unconventional.”
Bates nods, allowing her words to hang in the air. “Unconventional to the point of endangering yourself and your students, and committing acts of theft?”
Ms. Frizzle sighs. “Yes. It pains me to say it, but yes. The bus… the trip to Baltimore… the jewelry store… it was all a reckless, misguided attempt to further his scientific pursuits.”
Bates presses on, guiding Ms. Frizzle through the events that led to Sid’s arrest. He paints a vivid picture of the chaos and danger that Sid unleashed, emphasizing the emotional distress suffered by the children and the financial loss incurred by Samuelson’s Diamonds.
As Ms. Frizzle testifies, Sid sits at the defense table, his head bowed. He occasionally glances up at his former teacher, a look of remorse etched on his face. The weight of the charges against him, the potential consequences of his actions, seem to finally be sinking in.

Soon all of the class was put on the stand one by one, they all point to Sid as their kidnapper
One by one, the students of Walkerville Elementary take the stand. Arnold Perlstein, nervously clutching his inhaler, recounts the terrifying moments when the Magic School Bus careened through the streets of Baltimore. Carlos Ramon, ever the punster, makes a few ill-timed jokes about the situation, but his underlying fear is palpable. Dorothy Ann, meticulously documenting everything in her notebook, provides a detailed account of the events, her voice trembling slightly. Even Keesha Franklin, usually the most skeptical of the group, admits that she was genuinely frightened.
Each child, in their own way, points to Sid as the instigator of their ordeal. They describe how he hijacked the Magic School Bus, disregarding Ms. Frizzle’s warnings and pushing the vehicle to its limits. They recount the harrowing chase through the city, the near-misses with other vehicles, and the unsettling feeling that they were being used for something more than just a field trip.
As the children testify, the weight of their words bears down on Sid. He hangs his head, his face buried in his hands. The realization that he has betrayed the trust of his classmates, that he has caused them genuine fear and distress, is a heavy burden to carry.
The prosecution rests its case, confident that it has presented a compelling argument for Sid’s guilt. The defense now has its opportunity to present its side of the story.

Later Fred took the stand and pointed to Sid as the one who did this
The prosecution calls its next witness: Fred Jones, the mystery-solving icon. He takes the stand, looking more serious than his usual jovial self.
“Mr. Jones,” Ivan J. Bates begins, “can you please tell the court what you witnessed at Samuelson’s Diamonds & Estate Buyers in Baltimore on July 12th?”
Fred adjusts his ascot and leans into the microphone. “Well, like, it was a totally bizarre scene, man. I was just browsing for a gift for Daphne when this kid, Sid, and his… unconventional school bus showed up.” He points directly at Sid. “He had some kind of science gadget that made the Empress Diamond necklace disappear! It was like, poof! Gone!”
Bates presses him for more details, and Fred recounts the chaotic scene inside the jewelry store, emphasizing Sid’s role in the disappearance of the necklace. He reiterates that Sid was the one manipulating the device that caused the diamond to vanish.
Sid’s lawyer attempts to discredit Fred, questioning his reliability as a witness and suggesting that he may have misremembered the events. However, Fred remains steadfast in his testimony, insisting that he saw Sid commit the act.
The prosecution rests its case, feeling confident that it has presented overwhelming evidence of Sid’s guilt. The defense now has its opportunity to present its side of the story and attempt to cast doubt on the prosecution’s claims.

Later Ron Samuelson took to the stand and pointed to Sid as the kidnapper
The prosecution calls Ron Samuelson, CEO of Samuelson’s Diamonds & Estate Buyers, to the stand. He walks with a measured pace, his face etched with a mixture of anger and frustration.
“Mr. Samuelson,” Ivan J. Bates begins, “can you please describe the events that transpired at your store on July 12th?”
Samuelson takes a deep breath and recounts the chaotic scene, emphasizing the brazenness of the theft and the disruption it caused to his business. “That kid,” he says, pointing directly at Sid, “he waltzed in here with his… contraption and stole a priceless necklace right out from under our noses! He endangered my employees, terrified my customers, and caused irreparable damage to my reputation!”
Bates then asks Samuelson about the financial impact of the theft, eliciting testimony about the value of the Empress Diamond necklace and the losses incurred as a result of the incident. Samuelson’s anger is palpable as he describes the frustration of dealing with insurance companies and the uncertainty surrounding the recovery of the stolen gem.
During cross-examination, Sid’s lawyer attempts to portray Samuelson as a greedy businessman who is exaggerating the extent of his losses. However, Samuelson stands firm, insisting that Sid’s actions were a deliberate and malicious act of theft. He emphasizes that Sid not only stole the necklace but also held him and his employees hostage, effectively kidnapping them during the commission of the crime.
The prosecution rests its case, feeling confident that it has presented a compelling narrative of Sid’s guilt. The defense now faces an uphill battle as it attempts to poke holes in the prosecution’s case and convince the jury that Sid is not the villain he has been portrayed to be.

2 days later, the jury returned, the forman read the verdict as Sid stood: “We find Sid the Science Kid Guilty on all charges of 1st degree robbery and kidnapping
Two days later, the tension in the Edward A. Garmatz United States District Courthouse is palpable. Sid stands, his face pale and drawn, as the jury files back into the courtroom. The foreman, a stern-faced woman, holds the verdict in her hand.
Honorable Melissa Copeland asks, “Madam Foreman, has the jury reached a verdict?”
“We have, Your Honor,” the foreman replies, her voice steady.
“In the matter of The State of Maryland versus Sidney ‘the Science Kid’,” Judge Copeland says, “how do you find the defendant on the charge of first-degree robbery?”
The foreman takes a deep breath. “We find the defendant, Sidney ‘the Science Kid’, guilty.”
A gasp ripples through the courtroom. Sid’s lawyer puts his head in his hands.
Judge Copeland continues, “And how do you find the defendant on the charge of kidnapping?”
The foreman’s voice rings out, clear and unwavering. “We find the defendant, Sidney ‘the Science Kid’, guilty.”
Sid’s shoulders slump. The weight of the verdict crushes him. He looks around the courtroom, his eyes meeting those of Ms. Frizzle, who watches him with a mixture of sadness and regret.
The courtroom erupts in murmurs. The bailiffs move forward to take Sid into custody. His days of scientific exploration, at least for now, are over.

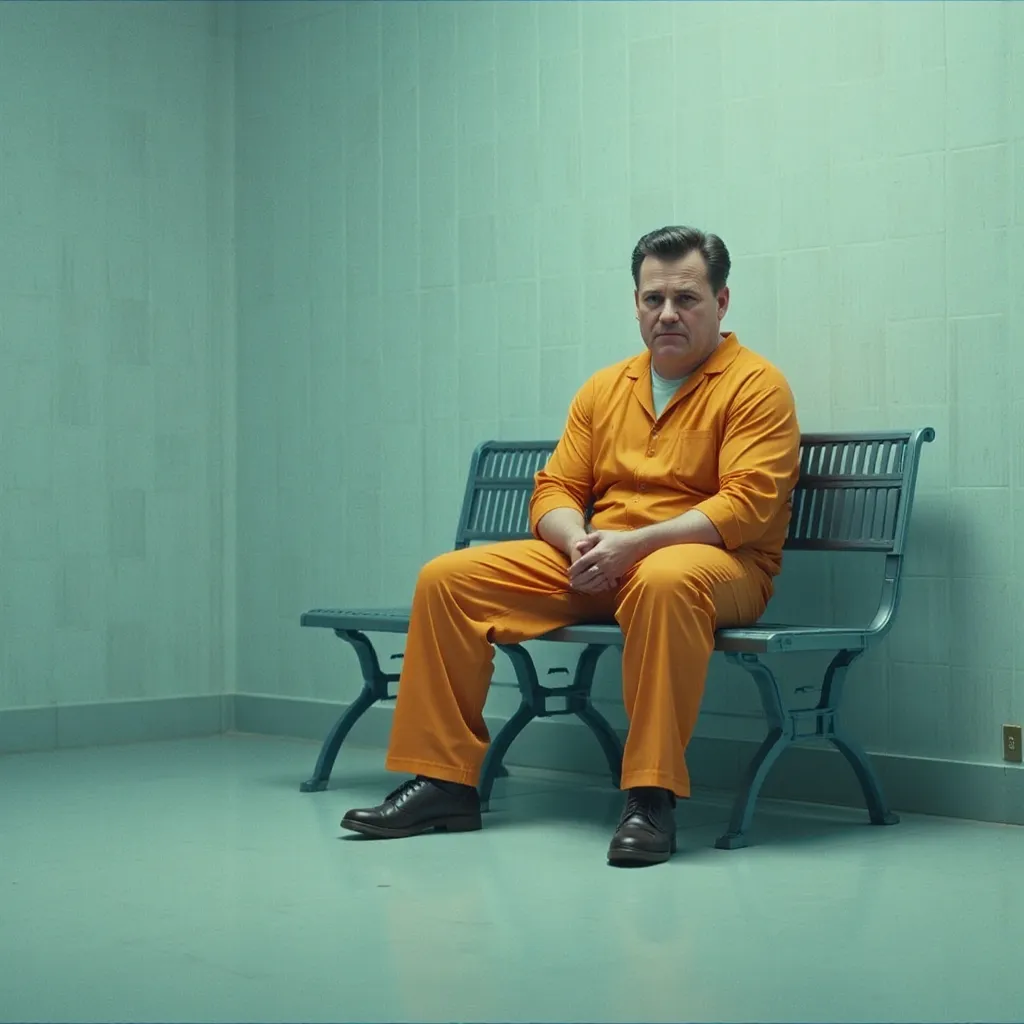
The judge soon orders Sid to sentenced to life at Ancora Psychiatric Hospital in Hammonton NJ
The courtroom falls silent as Judge Copeland delivers her sentence. Her voice is firm, devoid of emotion.
“Sidney ‘the Science Kid’,” she says, “the gravity of your crimes cannot be overstated. You endangered children, committed acts of theft, and displayed a shocking disregard for the law. While the court recognizes your intellectual capabilities, it also acknowledges the clear and present danger you pose to society.”
She pauses, her gaze fixed on Sid. “Therefore, this court sentences you to life imprisonment at Ancora Psychiatric Hospital in Hammonton, New Jersey. It is the hope of this court that you will receive the treatment you need and that you will never again pose a threat to the safety and well-being of others.”
A collective gasp fills the courtroom. Life imprisonment? At a psychiatric hospital? It’s a sentence that seems both harsh and unsettling. Sid stares at the judge in disbelief, his mind struggling to comprehend the enormity of what she has just said.
The bailiffs move forward, placing handcuffs on Sid’s wrists. As they lead him away, he looks back at Ms. Frizzle one last time, a flicker of despair in his eyes. She watches him go, her heart heavy with sorrow.
The courtroom empties, leaving behind the lingering echoes of a tragic case. A bright young mind, consumed by ambition and a reckless pursuit of knowledge, has been lost to the system. The consequences of his actions will haunt him for the rest of his days.
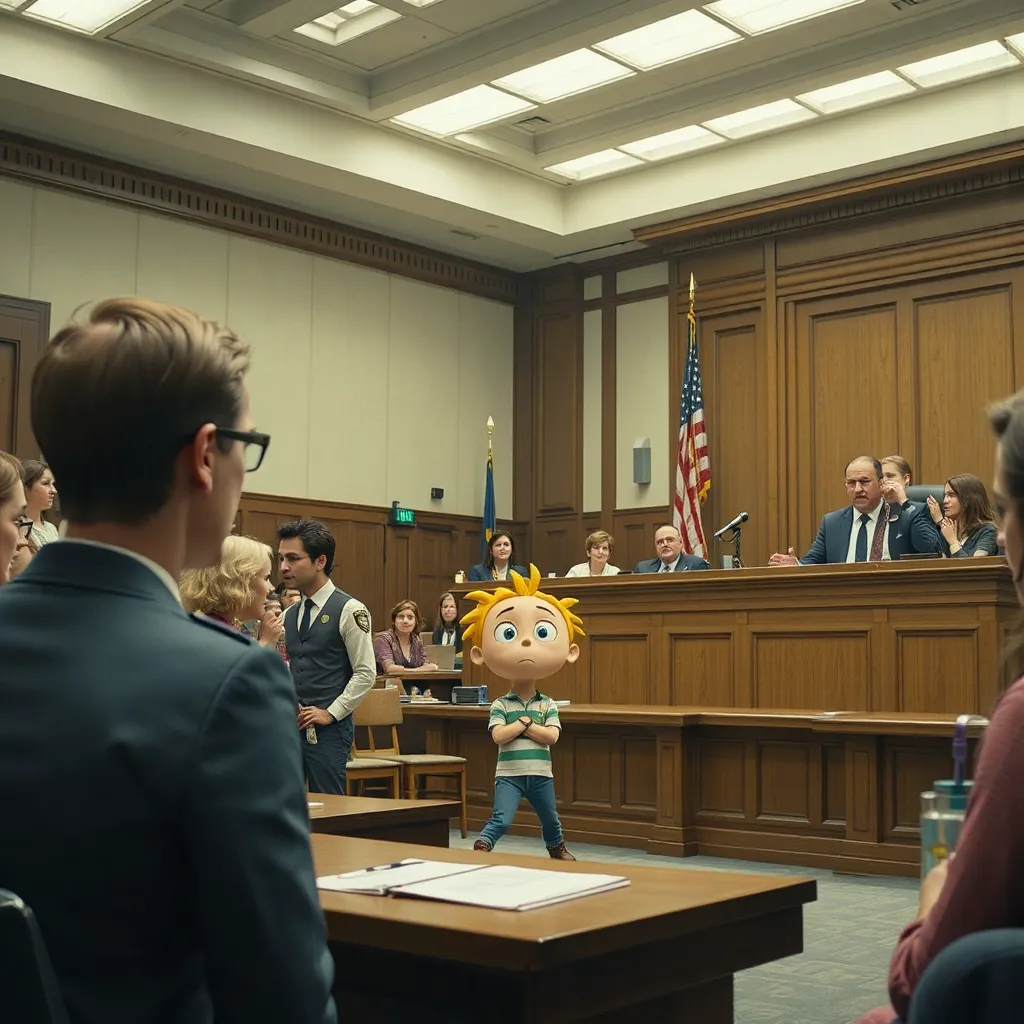

At the hospital one month later, Fred, Miss Frizzle and the class come to see Sid, Fred soon gives Sid a concussion time in his cell as the kids look on and laugh
One month later, a somber group gathers in the visitation area of Ancora Psychiatric Hospital. Ms. Frizzle, her usual exuberance replaced with a quiet sadness, leads her class. Fred Jones, looking uncharacteristically grim, accompanies them. They’ve come to see Sid.
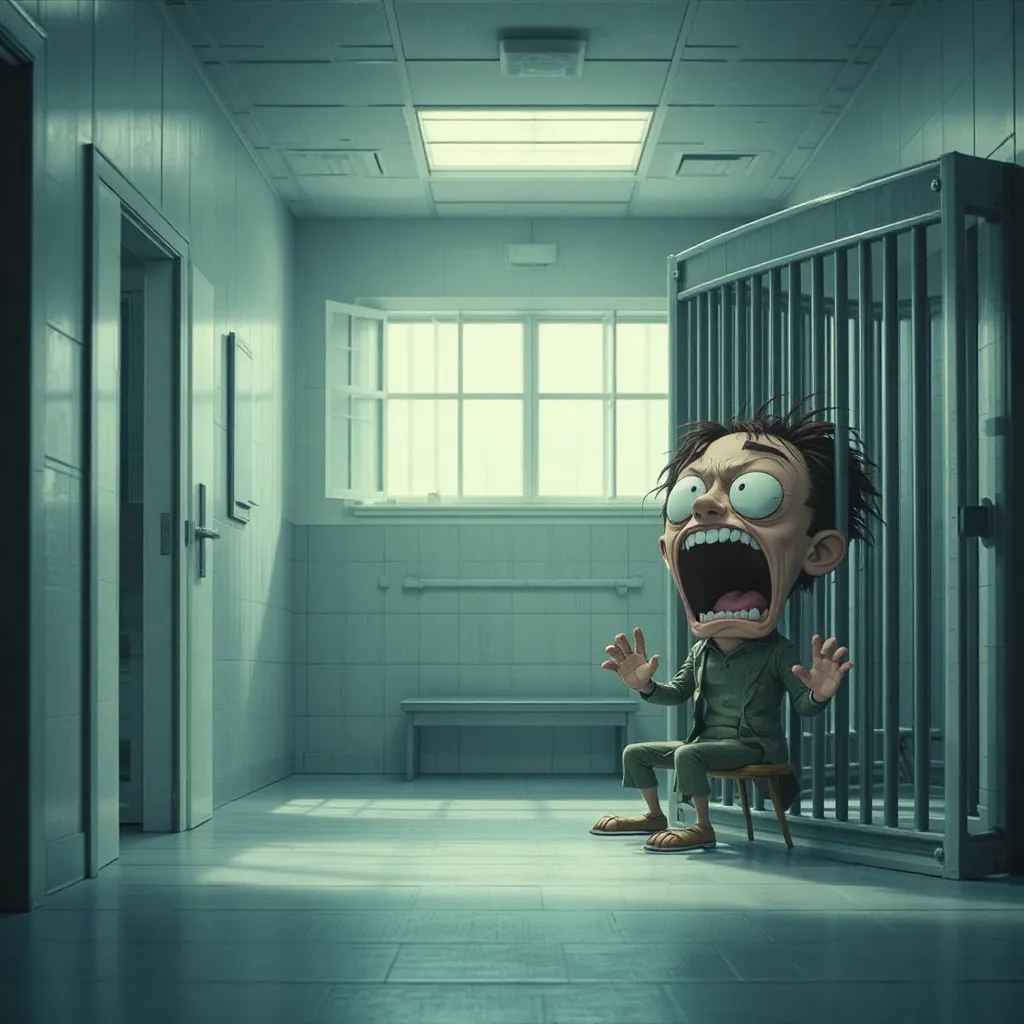
The heavy steel door clangs open, and Sid is led into the room. He’s wearing a drab hospital gown, and his eyes are vacant. He barely acknowledges their presence.
Ms. Frizzle steps forward, her voice gentle. “Sidney, we came to see you.”
Sid stares blankly ahead, muttering incoherently about refractive indexes and gravitational stress. The children shift uncomfortably, their laughter from the courtroom long forgotten.
Fred, his face contorted with anger, suddenly lunges forward. Before anyone can react, he delivers a swift punch to Sid’s head. Sid crumples to the floor, unconscious.
A collective gasp fills the room. Ms. Frizzle cries out in horror. The children stare in stunned silence, their eyes wide with a mixture of fear and excitement. Some of them begin to giggle nervously.
“Fred!” Ms. Frizzle exclaims, her voice trembling. “What did you do?”
Fred stands over Sid’s prone body, his chest heaving. “He deserved it,” he snarls. “He put those kids in danger! He stole that necklace! He needs to learn a lesson!”
The guards rush in, restraining Fred and dragging him away. Ms. Frizzle kneels beside Sid, checking for a pulse. The children watch, their laughter turning into nervous whispers. The visit has taken a dark and unexpected turn.
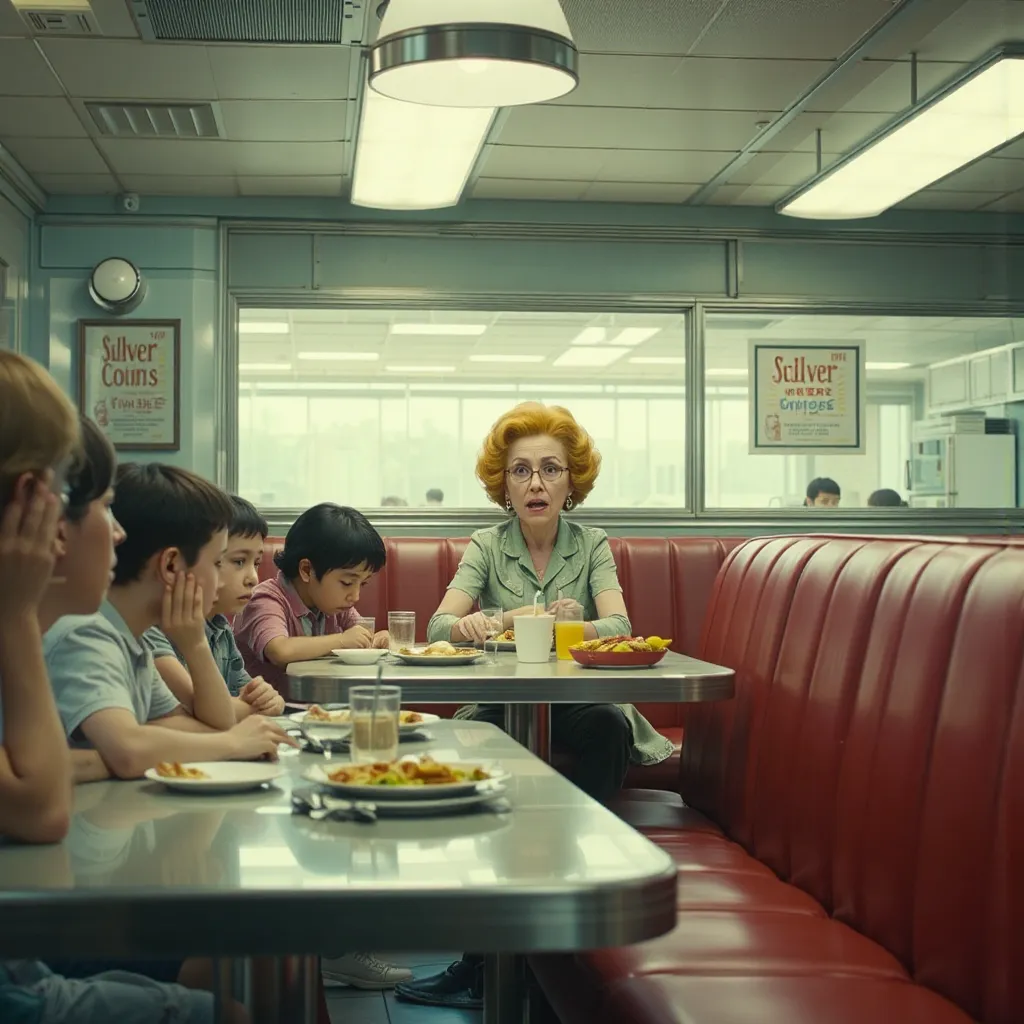
Fred soon takes Miss Frizzle and the kids over to Silver Coin Diner for dinner while Sid screams in his cell
The scene shifts to the Silver Coin Diner, a classic American eatery with red vinyl booths and chrome accents. Ms. Frizzle sits at a table, her face etched with worry. The children, still shaken by what they witnessed, are subdued, picking at their food. Fred is nowhere to be seen, presumably being questioned by the authorities.
Ms. Frizzle tries to put on a brave face, but her voice trembles as she speaks. “Alright, kids,” she says, forcing a smile. “Let’s try to forget about what happened and enjoy our dinner.”
The children nod weakly, but their hearts aren’t in it. The image of Sid lying unconscious on the floor is still fresh in their minds. The carefree days of scientific exploration seem like a distant memory.
Meanwhile, back at Ancora Psychiatric Hospital, Sid screams in his cell, his voice echoing through the sterile corridors. He’s alone, confused, and terrified. The punch to the head has only intensified his delusions, blurring the line between reality and fantasy. He rants about time travel, gravitational forces, and the injustice of his imprisonment. No one hears him, or if they do, they choose to ignore him. He is lost in the depths of his own mind, a prisoner of his own brilliance.